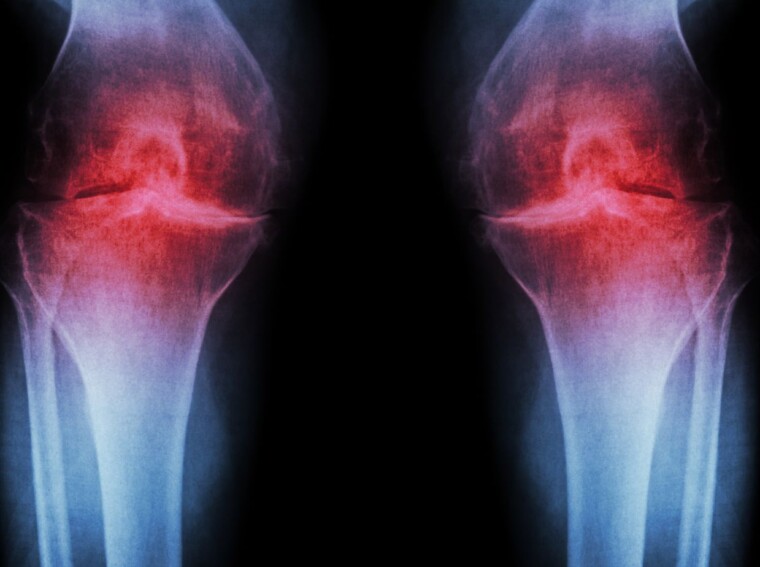
Osteoarthritis Of Knees ICD 10
Are you curious about the symptoms of osteoarthritis of knees according to the ICD 10 classification? Well, let me shed some light on this topic. Osteoarthritis is a common degenerative joint disease that primarily affects the knees. It is important to understand its symptoms as classified by the International Classification of Diseases (ICD) system, specifically ICD 10.
In ICD 10, the diagnosis code for osteoarthritis of knees is M17.1. This code helps medical professionals identify and classify this condition accurately. Now, let’s delve into the symptoms associated with this type of knee osteoarthritis.
The most prevalent symptom experienced by individuals with osteoarthritis of knees is joint pain and stiffness. The pain may be localised to one or both knees and can vary in intensity from mild discomfort to severe agony. Stiffness tends to worsen after periods of inactivity or prolonged sitting.
Additionally, swelling and tenderness around the affected knee joints are common manifestations. You may notice an increase in fluid accumulation within the joint, leading to visible swelling and a feeling of warmth or tenderness when touching the area.
Understanding these symptoms can help individuals recognize if they might be experiencing osteoarthritis of knees according to ICD 10 guidelines. If you suspect you have this condition, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional for accurate diagnosis and appropriate management strategies tailored to your specific needs.
Understanding Osteoarthritis of the Knees
Osteoarthritis of the knees, also referred to as degenerative joint disease, is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is important to understand the symptoms and implications of this condition to seek appropriate treatment and manage its impact on daily life.
What is Osteoarthritis? Osteoarthritis is a type of arthritis characterised by the gradual breakdown of cartilage in the joints. In the case of knee osteoarthritis, the protective cartilage cushioning the ends of bones in the knee joint gradually wears away over time. This can lead to pain, stiffness, swelling, and reduced mobility in affected individuals.
The Role of ICD 10 Codes ICD 10 codes are used by healthcare professionals for proper diagnosis and coding purposes. The specific ICD 10 code for osteoarthritis of the knees is M17.x (where “x” represents additional characters). These codes help healthcare providers accurately identify and track different types and stages of osteoarthritis.
Common Symptoms The symptoms experienced by individuals with knee osteoarthritis can vary from mild discomfort to severe pain that hinders everyday activities. Some common symptoms include:
- Joint pain: Persistent pain or aching in and around the knee joint.
- Stiffness: Difficulty in bending or straightening the knee.
- Swelling: Visible swelling or fluid accumulation around the affected area.
- Limited range of motion: Reduced ability to fully extend or flex your knee.
- Grating sensation: A rough feeling or noise when moving your knee.
Risk Factors Several factors contribute to an increased risk for developing osteoarthritis in your knees:
- Age: The likelihood increases with age as wear-and-tear on joints accumulates over time.
- Obesity: Excess weight places added stress on weight-bearing joints like the knees.
- Joint injuries: Previous knee injuries, such as fractures or ligament tears, can raise the risk.
- Genetics: Family history of osteoarthritis may predispose individuals to develop the condition.
Treatment Options While there is no cure for knee osteoarthritis, various treatment approaches can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. These include:
- Pain relievers: Over-the-counter or prescription medications to alleviate pain.
- Physical therapy: Exercises and techniques to strengthen muscles around the knee joint and increase flexibility.
- Assistive devices: The use of braces or walking aids to reduce pressure on the knees.
- Lifestyle modifications: Maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in low-impact exercises, and avoiding activities that aggravate knee pain.
Understanding the symptoms and impact of osteoarthritis of the knees allows individuals to seek appropriate medical attention and adopt strategies for managing this condition effectively. If you experience persistent knee pain or suspect you may have osteoarthritis, consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalised treatment plan.